Procurement has many steps from sourcing suppliers and the many steps in between to the good being delivered or service provided and then paid for. All state agencies, boards, or commissions use procurement in one way or another. The strategic use of procurement can greatly help each organization fulfill their individual missions.
Public Procurement VS. Private Procurement
Public and Private procurement occurs under very different circumstances, even though they’re both named procurement:
Public Procurement is procurement that is completed within the context of not-for-profit organizations, also known as the public sector, or the procurement that occurs in this context is typically government affiliated (which can be central, state, or local). Public procurement is typically driven by government entities, there is limitations to the flexibility in their spend and methods of funding. Public sector procurement is required to be conducted in more transparent contexts. This comes in the form of regulations and legislation requiring public entities to report back to the government (and the people) with how money is being spent.
Private Procurement that is completed within the context of for-profit organizations and it happens within privately owned companies; also known as the private sector. As for the private sector, there is much more room for flexibility and agility within budgeting and has a focus on driving revenue. This typically results in less sustainable methods of procurement; considering there is less need for a focus on social responsibility.
Below, the Procurement processes are broken into two main processes: Sourcing and Purchasing
What is Sourcing?
The identification and selection of the supplier whose costs, qualities, technologies, timeliness, dependability, and service best meet the organization’s needs.
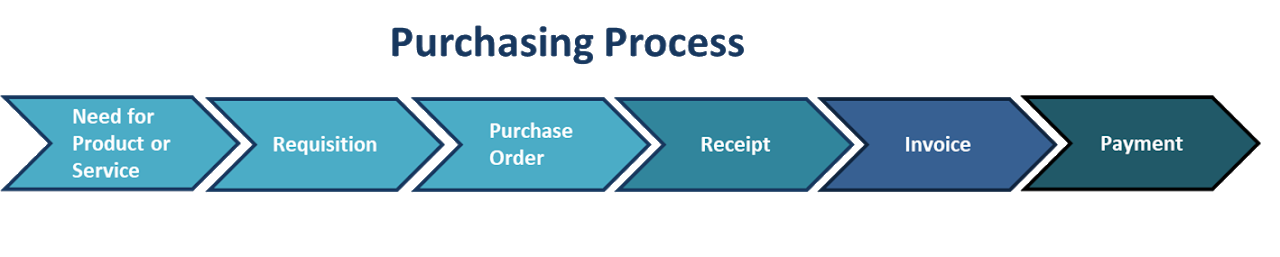
Need for Product or Service: Determine specifics of product or service needs and locate on specific state contract
Requisition: Specify these needs in a Requisition and submit for appropriate approval
Purchase Order: The approved Requisition becomes a Purchase Order and is sent to the supplier to order goods/service
Receipt: After Goods are received/Services are performed a receipt of those goods/services is created
Invoice: Supplier submits an invoice to the state who matches it with the Receipt
Payment: Upon approval of these purchasing documents payment is then made to the supplier
Formal Solicitation Process
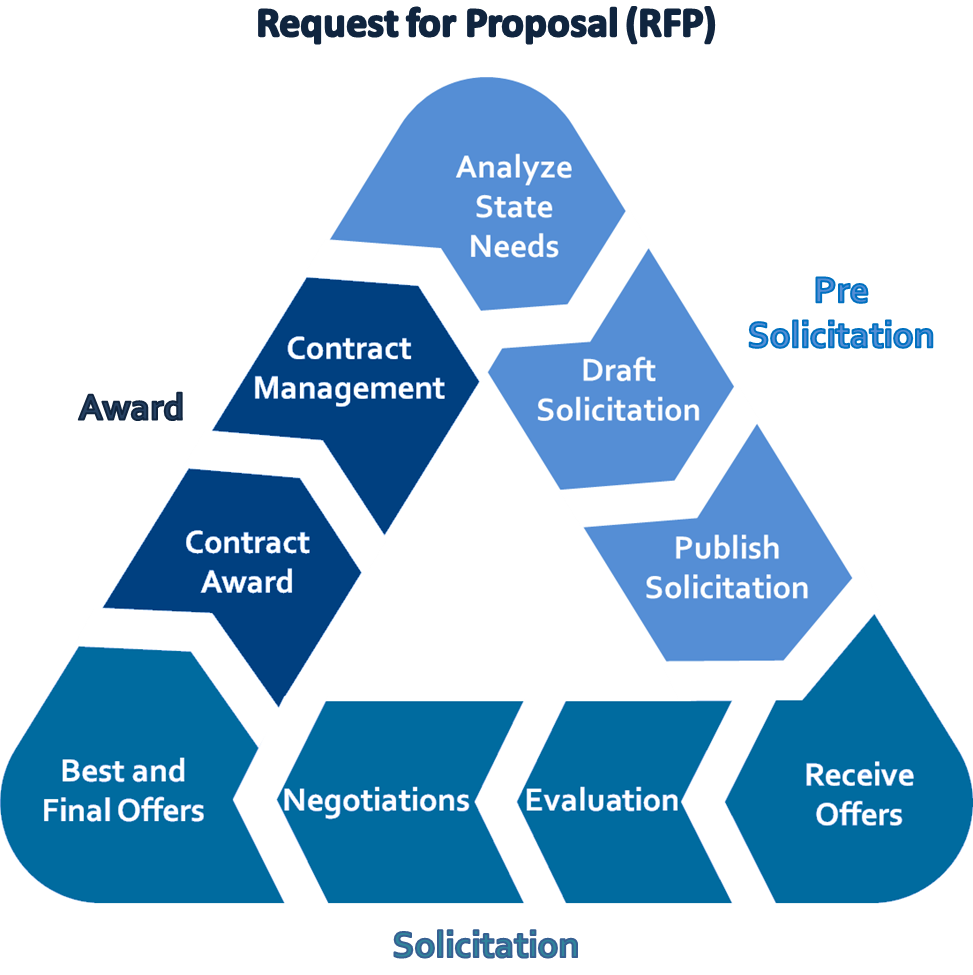
Pre-Solicitation
- Analyze State Needs: Define needs/confirm funding and research available options in the marketplace
- Draft Solicitation: Prepare specifications and/or statement or scope of work with contract users
- Publish Solicitation: Solicitations posted in APP; Changes made to solicitation formalized in amendments, Questions answered, Conduct pre-offer conference
Solicitation
- Bid Closes: Receive and open offers, Review for responsiveness and responsibility
- Evaluation: Procurement Officer and evaluation committee meet to evaluate responses
- Negotiations: Based on approved Negotiation Plan, hold negotiations with shortlisted bidders
- Best and Final Offers: Re-Open Solicitation; Allow shortlisted bidders to submit revised responses
- Contract Award: Contract award posted in APP; Procurement file becomes public
Post Award
Contract Management: On going assessment of supplier relationship and contract performance
What is a Request for Proposal (RFP)?
A Request for Proposal (RFP) is a solicitation document issued by an organization to request bids for products, solutions and services. It is intended for procurements of $100,000 and greater in aggregate value where the State seeks Best Value over Low Bid.
What is a Request for Quotation (RFQ)?
A request sent to suppliers along with a description of the commodity or services needed and the supplier is asked to respond with price and other information by a predetermined date. Evaluation and recommendation for award should be based on the quotation that best meets price, quality, delivery, service, past performance, and reliability. Purchasing method generally used for purchases estimated to exceed $10,000 but less than $100,000.
What is an Invitation for Bids (IFB)?
A procurement method used to solicit competitive sealed bid responses, sometimes called a formal bid, when price is the basis for award. This process is used in procurements of $100,000 or greater where the contract is awarded to lowest responsible and responsive bidder.
What is a Sole Source Procurement?
A non-competitive method of procurement used when only one supplier possesses the unique ability or capability to meet the particular requirements of the entity or because only one supplier is practicably available. The entity may require a written justification from the end user explaining why only this supplier can fulfill the requirement.
What is a Task Order Contract?
An indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity contract for supplies or services that provides for the issuance of Task Order (TO) for services or supplies during the contract period.